Main Differences between Batteries and Capacitors
A Battery and a Capacitor is similar as both store and release the electrical energy and rated in Ah. But, there are some key differences between them which has been discussed in the following post. The main difference between a battery and a capacitor is that Battery stores charge in the form of chemical energy and convert to the electrical energy whereas, capacitor stores charge in the form of electrostatic field.
Battery
A Battery is a device used as source of energy. It has three main parts known as Cathode (Positive Terminal), Anode (Negative Terminal) and a separator known as electrolyte. Battery store energy in the form of chemicals and convert it back to the electrical energy when needed. The chemical reaction called oxidation-reduction takes place in between the cathode and the anode via the separator (electrolyte) during charging and discharging of the battery.
Capacitor
A Capacitor is a two terminal device having two or more parallel layers plates separated by a dielectric medium known as insulator. When voltage applied across the plates of capacitor, current want to flow through it until the voltage across both the negative and positive (Anode and Cathode) plates become equal to the applied voltage (source). The insulating medium in between the two conductive plates of capacitor opposes to the flow of current. This change create an effect which stores in capacitor in the form of electrostatic field.
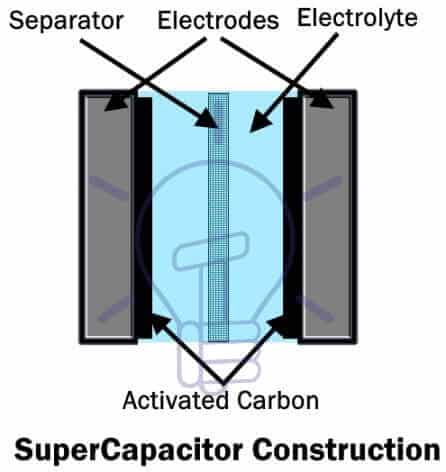
Super-capacitor
A super-capacitor is also known as Super Cap or Ultra-Capacitor. It is a type of polar capacitor with high capacitance rating but has low voltage rating. Super-capacitor capacitance ranges from 100 F to 12000 F with low voltage ratings approximately 2.5 v to 2.7 v.
Super-capacitor is supposed to be in between a Capacitor and battery. These types of capacitors charge much faster than a battery and charge more than an electrolytic capacitor per volume unit. That is why a super-capacitor is considered between a battery and an electrolytic capacitor.
Main Differences Between a Battery and a Capacitor
The following table shows key differences and comparison between capacitors and batteries.
| Characteristics | Battery | Capacitor |
| Symbol | 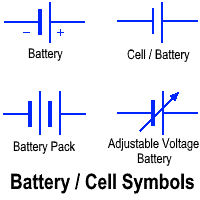 |  |
| Definition | Battery stores potential energy in the form of chemical energy which is later converted to the electric energy. | A Capacitor stores the potential energy in the form of eclectic field (electrostatic field) and release to the circuit as electric energy. |
| Construction | Battery has three parts known as Cathode (positive (+ve), Anode (Negative (-ve) and Separator (known as electrolyte). | Capacitor is a simple two terminal device Terminals are metallic plates and there is a dielectric material (insulator) between them. |
| Function | Batteries provide energy to the connected circuits. i.e. Battery generates electrons and charge. | Capacitors draw, store and release the energy. i.e. Capacitor only stores charged electrons. |
| Working Principle | Battery works based on chemical reaction called oxidation-reduction reaction. | When voltage applied across the capacitor terminals, It starts to store energy in it. |
| Operation | Battery Generate Electrons. | Capacitor Store Electrons. |
| Types | Battery types are Alkaline, Lithium Cells, Silver Oxide Cells, Zinc Air Cells, Zinc Carbon, Lead Acid, Lithium Ion (Li-ion), Nickel Metal Hydride (Ni-MH), Nickel Cadmium (Ni-Cd) etc. | Electrolytic, Electrostatic, Electrostatic, Electrochemical, Super Capacitor, Hybrid Super Capacitors, Ceramic Capacitors, Film Capacitors, Tantalum, Integrated Capacitor. |
| Type of Device | Battery is an Active Component. | Capacitor is a Passive Component. |
| AC & DC Usage | Battery is used to provide DC supply. | Capacitor blocks DC supply and pass the AC supply. |
| Voltage Behavior | A battery provides almost constant voltage while discharging. | A Capacitor discharging voltage quickly decreased. i.e. discharge rate is very fast. |
| Potential Difference (P.d) | Constant | Increases exponentially |
| Charging and Discharging | The Charging and Discharging time of a Battery is slow i.e. 10 – 60+ minutes. | Charging and Discharging time of a Capacitor is very fast i.e. 1-10 seconds. |
| Charging Temperature | 0 – 45 °C (32 – 113°F) | -40 to 65 °C (-40 – 149°F) |
| Life Cycle | 500+ Hours | 1M – 3M hours. |
| Service Life | 5-10 Years | 10-15 Years |
| Voltage per Cell | 3.6-3.7 Volts | 2.3 – 2.75 Volts. |
| Specific Power Rating | Battery Specific power rating is about 1k – 3k (W/kg). | Capacitor Specific power rating is about 1M (W/kg). |
| Polarity | Battery polarity reversed during charging and discharging. | Capacitor polarity must be same during charging and discharging. |
| Size | For the same charging capacity, Battery size is small as compared to a capacitor. | Capacitor size is large as compared to a battery for same capacity rating. |
| Cost | Cost of Battery is higher. | Cost of Capacitor is Less. |
| Advantages |
- Storage Capability
- Power Density
- Better Leakage Current than a Capacitor
- Constant Voltage
|
- Long Life Cycle
- Short Charging Time
- High Load Currents
- Good Temperature Performance
|
| Disadvantages |
- Limited Life Cycle
- Long Charging Time
- Currant and Voltage Limitation
- More Temperature sensitive
|
- Low Specific Energy
- High Self Discharge
- High Cost per Watt as compared to Battery
- Linear discharge voltage during operation
|
| Applications |
- Power Electronics
- Household application
- Storage the power
- Medical devices
- IOT based devices
- Military and submarines
- AI based devises
- Used in automotive Vehicles
- Used as backup power supply restoration.
|
- Smoothing power supply’s output.
- Power factor correction
- Frequency filters, high pass, low pass filters.
- Coupling & Decoupling of signals.
- Motor Starter.
- Snubber (Surge absorber & Noise filter)
- Oscillators
|
Related Posts:







No comments